Technical assistance
We want to clear the main technical questions that may arise about the operation of our products and the steps necessary for their assembly.
Lighting
In order to facilitate and make the characteristics of the different items more visual, you can find a series of icons or symbols associated with each item that define its main characteristics. At the start of each family you will find the explanatory legend, or by clicking above the icons on the website.

The main difference between colour temperatures on lights is their Kelvin degrees and light colour. - The temperature of cool white is between 5,100 and 7,000 Kelvin and it has a blueish colour. - The temperature of the natural colour is between 4,000 and 5,000 Kelvin and it has a neutral colour. - The temperature of warm white is between 3,000 and 3,900 Kelvin and it has an orangey colour.

Lighting with a natural white colour temperature is between 4,000 and 5,000 Kelvin and its light colour is neutral.
The following image outlines the types of voltage and frequency that are used in each country in the world in domestic environments:For further information, look up

The following image outlines the types of plug socket and power supply that are used in each country in the world in domestic environments:

IP44 is the name given to the index that a light or component has in order to protect itself against objects larger than 1 mm and that also have protection from liquid splashes in all directions. In this case, depending on the area where the lighting is located, it would be suitably for assembly in bathroom furniture.
IP20 is the name given to the index that a light or component has to protect itself from objects larger than 12.5 mm, but without protection against liquids. In this case, said lighting would be suitable for assembly in home furniture.
IP (Ingress Protection Rating) is the name given to the index of a light or component to protect itself or not be damaged by dust or water. For example, the ideal lights for lighting bathrooms have IP44 protection. The first digit of the index is the protection from solids and the second digit of the index is protection from liquids. Protection from solids: IP0X: Without protection. IP1X: Protection from objects larger than 50mm, for example a hand. IP2X: Protection from objects larger than 12.5mm, for example a finger. IP3X: Protection from objects larger than 2.5mm, for example a screwdriver. IP4X: Protection from objects larger than 1 mm, for example a cable. IP5X: Protection from dust, limited intake allowed. IP6X: Protection from concentrations of dust. No dust intake is allowed. Protection from liquids: IPX0: Without protection. IPX1: Protection from the fall of vertical liquids, limited intake allowed. IPX2: Protection from the vertical fall of water with the product inclining at a 15° vertical angle, limited intake allowed. IPX3: Protection from water spray at a 60° vertical angle, limited intake allowed. IPX4: Protection from liquid splashes in all directions, limited intake allowed. IPX5: Protection from jets of water, limited intake allowed. IPX6: Protection from strong jets of water, limited intake allowed. IPX7: Protection for immersion of 15cm to 1 m for 30 min, no water intake is allowed. IPX8: Protection for continuous immersion underwater.
In a bathroom fitting, lights and components must comply with a series of characteristics that take into account the areas of the bathroom where they are located. Therefore, we will restrict ourselves to four existing volumes in the bathroom: Volume 0: It encompasses the area inside the bath or the shower. Volume 1: It is delimited by the horizontal plane higher than volume 0 and the horizontal plane located 2.25 m above the ground, delimited by the vertical plane around the bath tub or shower. Volume 2: This encompasses the vertical plane outside of volume outside of volume 1 and the parallel vertical plane located at a distance of 0.60m, delimited by the horizontal plane located 2.25 m above the ground. Volume 3: It is delimited by the outer vertical plane of volume 2 and the parallel vertical plane located at a distance of 2.4 m from the latter, it is delimited by the horizontal plane located 2.25 m above the ground, or up to a height of 3 m, if the roof is at that height or more from the ground. PLEASE NOTE: False roofs and screens are not considered to be barriers for the purposes of separating these volumes.Consequently, lights and components that may be installed in each of these volumes are as follows according to the degree of protection. Volume 0: It is possible to install lights and components with IPX7 protection. Volume 1: It is possible to install lights and components with IPX4 protection. For IPX2 protection, installation can take place if above the highest level of the fixed shower diffuser. IPX5 protection can be installed in hydromassage baths and in public baths where jets of water may be produced during cleaning. As well as devices powered by SELV no higher than 12 V ac or 30 V cc. Volume 2: It is possible to install what is allowed under volume 1. As well as lights whose power supply has differential current protection of a value not higher than 30mA, according to regulation UNE 20.460-4-41. Volume 3: It is possible to install lights and components with IPX5 protections, in shared baths where jets of water may be produced during the cleaning of them. In addition to lights protected by an isolation transformer, or by SELV, or by differential current protection of a value not higher than 30 mA, according to regulation UNE 20,460-4-41. PLEASE NOTE: Public baths are those found in schools, factories, sports centres, etc., and all those used by the public in general.

In an installation for home furniture, lights and components must comply with a series of characteristics:They must have class II insulation, be protected against electric changes through direct and indirect contact, an earth connection is not necessary. Or they can have class III insulation, and should therefore not be connected to an earth connection.Also, they have to be able to be installed on surfaces with materials that are not known to be inflammable, such is the case with wood. Or, they should be suitable for installing on surfaces that are normally inflammable.

The power tolerance should be -20% in power supplies. That is to say, if the total power of lights connected to a single converter is 12 W, it is necessary to use a 15 W converter. However, if the installation surpasses 12 W, it is necessary to choose a more powerful converter, for example 30 W.
No, they are isolated converters. Therefore, they do not need to be earthed.
Yes, the converters with metal casing need to be earthed and include a specific terminal for connection.
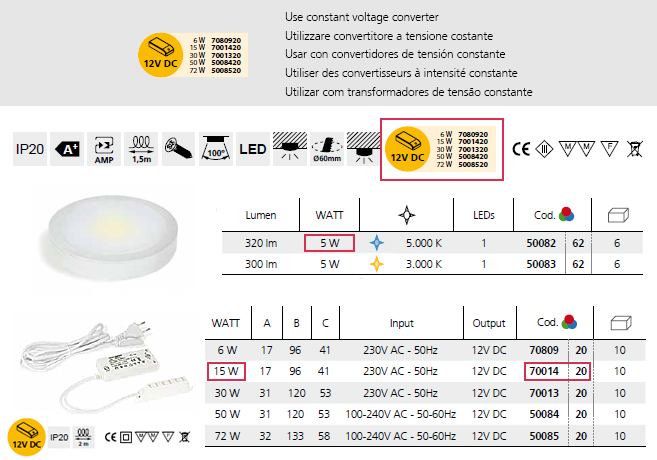
In order to choose the correct converter or transformer for each light, it is necessary to:1\. - Know the type of converter or transformer that corresponds to each light (12V DC, 350 mA or 12V AC). In our catalogue we indicate on each light the type of converter or transformer that must be used through a series of icons.2\. - Know the total necessary power (6 W, 15 W, etc.). Once you have chosen the type of converter you have to choose the power that is required. For that purpose, it is necessary to add up all the powers of the lights that you are going to connect to the same converter.For example, you have 4 Orion lights (code 7048162) each 3 W, the total power is therefore 12 W. It is recommended that the converters work at 80% of the maximum power that they withstand. Therefore, we will choose the 15 W LED converter (code 7001420).Likewise, the maximum number of lights that can be connected to the same converter is 6 units, as the AMP distributors have 6 connectors.
If an LED light does not turn on it is because it needs more power than that provided by the converter or it may be due to a polarity problem.In this case lights connected to a direct current have to maintain polarity throughout the entire circuit (positive with positive and negative with negative).

If an LED light switches on and then switches off, it is because the converter is overheating.The most common reasons for the converter to overheat are a lack of ventilation in the place of installation or excessive power delivery.In this case the converter is providing all or more of the power that it can give and we will need to replace it with a more powerful converter.
An LED light may flicker for several reasons, in order to know the cause, you must:Check that the LED light is connected to the correct type of converter, constant voltage or constant intensity.Check that the power of the converter is not less than the total power of the LED lights connected to the converter.Check that that the converter is not overheating. The converter needs to have a suitable operating temperature. The operating temperature is printed on the converter.











